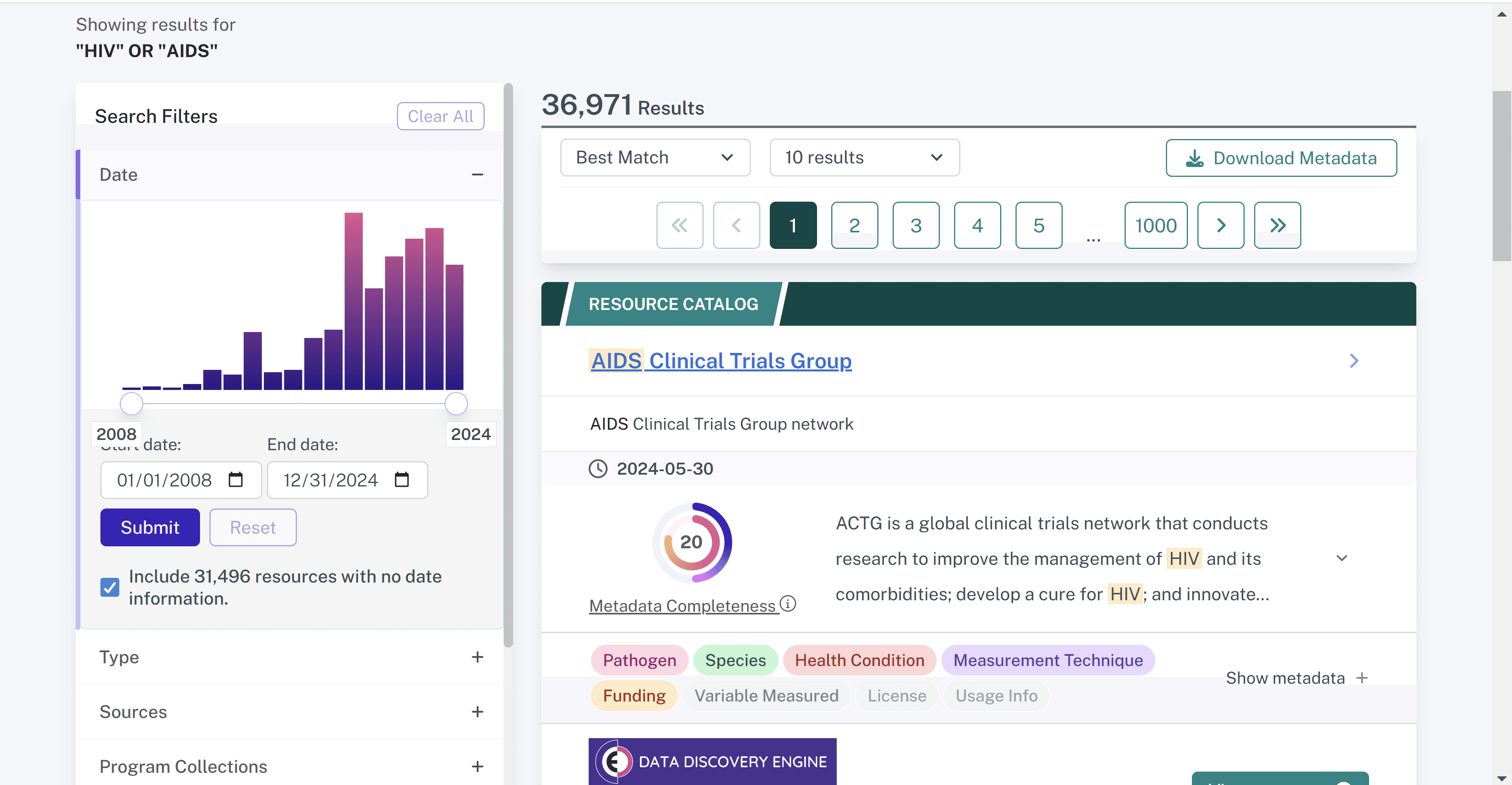
Filtering results
The Discovery Portal provides filtering options to help you narrow down search results and find the most relevant datasets, tools, or resource catalogs. Filters are available on the left side of the search results page and can be applied individually or in combination. Each filter category can be expanded or collapsed to make it easier to navigate. The number of results for each term is displayed next to each term within each filter.
As an example, if a researcher wanted to narrow the search for HIV / AIDS resources to only include Expression profiling by high throughput sequencing datasets from NCBI GEO, they could select the "NCBI GEO" checkbox under Source and "Expression profiling by high throughput sequencing" under Measurement Technique. This will update the search results and the count of records in the filters.
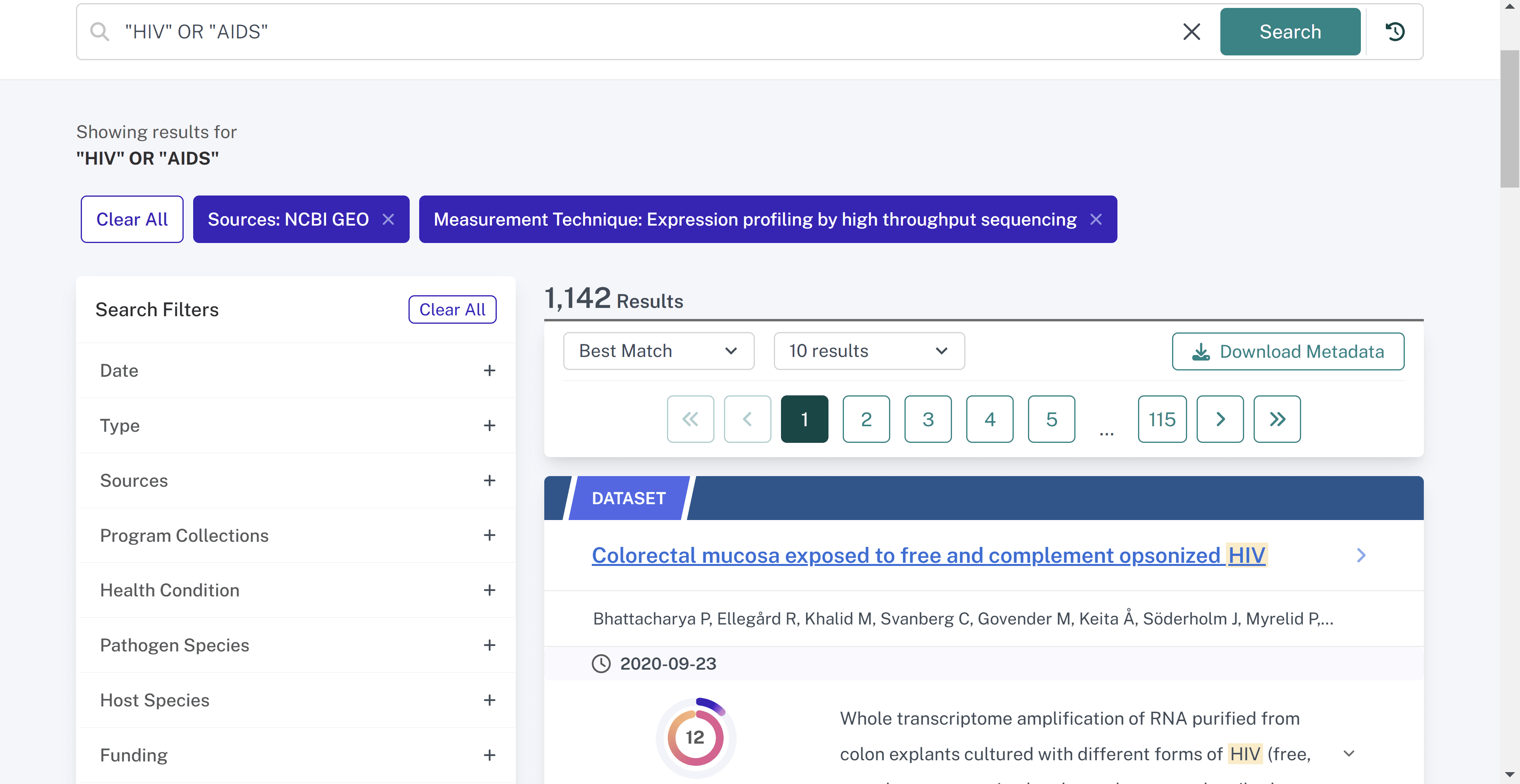
At the top of the page there are buttons for the filters applied; clicking on the "X" will remove that particular filter.
📘 What happens if I select multiple items from the same group or different filter groups?
Selecting items from multiple filter groups looks for both of those filters
Selecting checkboxes from two separate filters — like Source and Measurement Technique in the example above — will provide only the records which fulfill both those conditions, like NCBI GEO and Expression profiling by high throughput sequencing.
Selecting within a group looks for any of those filters
Selecting multiple Measurement Techniques, for example, would look for either of those conditions, like Expression profiling by high throughput sequencing or CyTOF.
What can I filter by? #
Filters common to all resources: #
Date
Describes the most recent date from date created, modified, or published. Use the date histogram to filter by year or filter to a date range by manually entering a start and end date and hitting 'Submit.' The results will automatically include all resources that do not contain date metadata until you apply a date filter or deselect 'Include resources with no date information.'
Type
Describes the category of the resource. Use this filter to narrow down results by categories like Datasets, Resource Catalogs, or Computational Tools.
Source
Use the Source filter to narrow down where the original metadata comes from. This is a required field for every resource. See Where does the data come from?
Funding
Use Funding to filter by the funding agency and/or grant number that help fund the resource creation. Multiple grants/contracts/awards can apply to a given resource, and often, the funding information is missing for a resource.
Conditions of Access
Use Conditions of Access to filter by resource accessibility. Resources may be open, closed, or have restricted or embargoed access. This information may also be missing for many resources.
Filters for Datasets: #
Program Collections
Program Collections are datasets contributed by specific NIAID programs and research initiatives. Use the Program Collections filter to quickly find datasets that are part of specialized research efforts. For example, you can use this filter to see datasets contributed by the CREID Network. You can read more about Program Collections here.
Health Condition
Use the Health Condition filter to narrow down the health conditions or infectious diseases which are the focus of the resources. For example, a researcher could use this filter to quickly find all resources where 'tuberculosis' is listed as the health condition.
Pathogen Species
Use the Pathogen Species filter to narrow down the infectious agents or pathogens which are the focus of the resources. For example, a researcher could search for influenza resources and filter by just 'h1n1 subtype' or 'h5n1 subtype.'
Host Species
Use the Host Species to filter by the species or host organisms from which the resources have been created. For example, a researcher could narrow their search for COVID-19 resources to 'homo sapiens' if they are only interested in human data.
Variable Measured
Use the Variable Measured filter to narrow results to specific variables measured by resources. Each resource may have one, many, or no variable measured metadata associated with it. For example, a researcher could narrow their search for malaria to proteomics resources.
Measurement Technique
Use Measurement Technique to filter by the experimental or analytical techniques used to generate resources. Each resource may have one, many, or no measurement techniques associated with it. For example, a researcher could filter their influenza search to flow cytometry resources.
Filters for Computational Tools: #
Application Category
Use the Application Category filter to narrow down resources by their type of software application. For example, a researcher could use this filter to find ‘Command line tools,’ Web applications,’ a ‘Library,’ ‘Web API,’ or other applications.
Operating System
Use the Operating System filter to narrow down resources by the operating system they are suited for. For example, a researcher could use this filter to find tools for ‘Windows’, ‘Mac,’ ‘Linux,’ or other operating systems.
Programming Language
Use the Programming Language filter to narrow down resources by the coding languages used in the development of software tools or analysis pipelines. For example, a researcher could use this filter to find computational tools developed in ‘Python’ or ‘R’.
Feature List
Use the Feature List filter to narrow down computational tools according to the features or modules they provide. For example, a researcher could use this filter to find ‘genotyping’ tools, ‘haplotype mapping’ tools, ‘SNP detection’ tools, or tools with other features.
Input
Use the Input filter to narrow down computational tools according to their required software input, such as a file or parameter. For example, a researcher could use this filter to find tools in which they could input a protein sequence, gene ID, or something else.
Output
Use the Output filter to narrow down computational tools according to the output they generate. For example, a researcher could use this filter to find tools that output sequence reports, protein features, or something else.
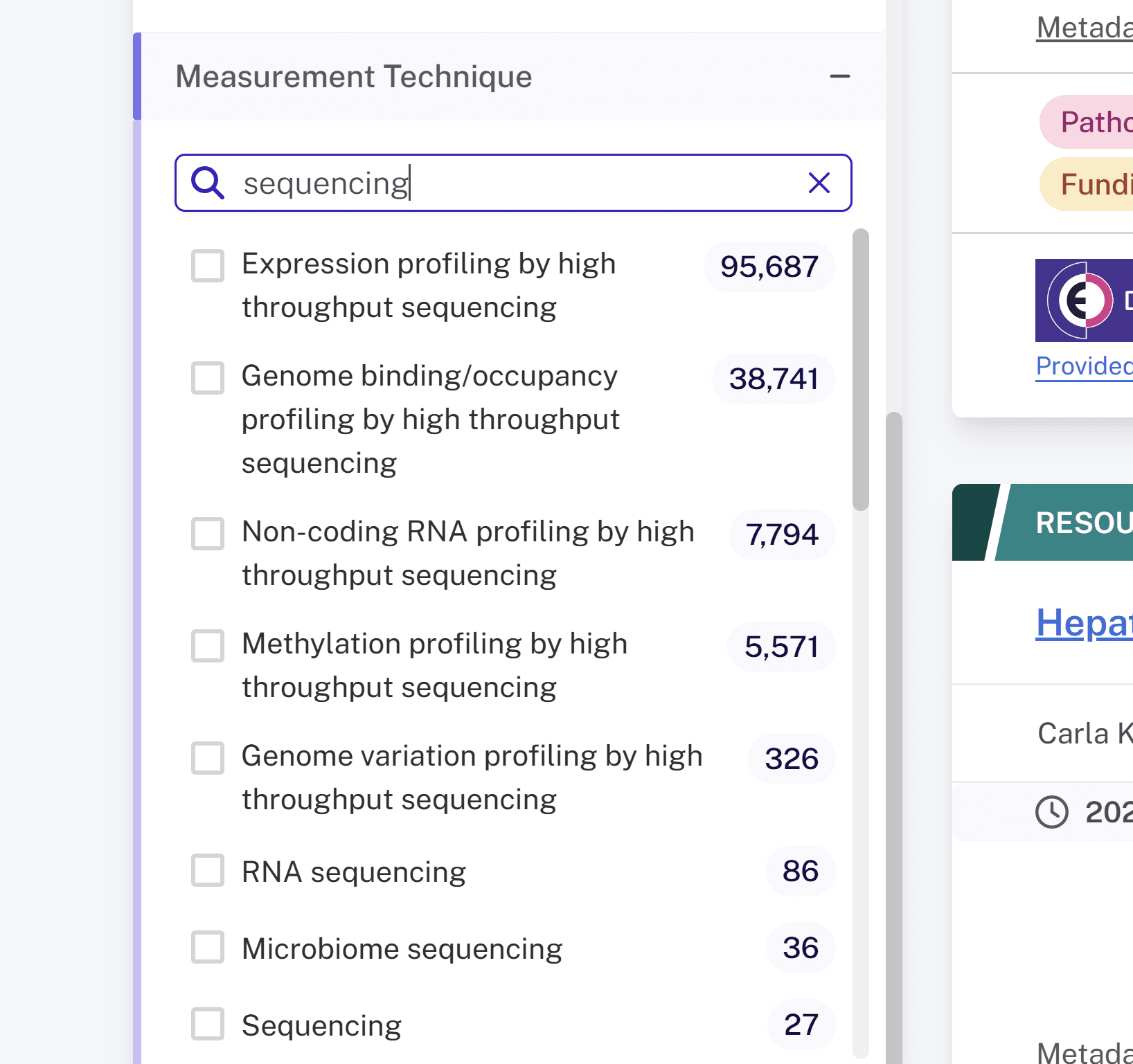
Searching within a filter #
There is a search bar within each filter to find particular terms. For example, a user could open the Measurement Technique panel and enter "sequencing" in the search bar to list only the measurement techniques related to sequencing.
Selecting 'Not specified' #
Metadata does not exist for many fields in every resource. Within each filter, select 'Not specified' to get all of the results for a query that do not have metadata for that field. For example, if a researcher was interested in influenza prevalence in dogs and found that the Host Species filter had 6 results for Canis lupus familiaris, they could select "Not specified" to search across the remaining resources to see if there are additional relevant resources.
Selecting 'Any specified' #
Within each filter, select 'Any specified' to get all of the results for a query that have any metadata for that field. For example, if a researcher was interested in influenza resources and needed to see the funding information but did not necessarily care who the specific funder was, they could search 'influenza' and then select "Any specified" to see all influenza resources that have funding information.
Key takeaways to help you get the most out of filtering in the Discovery Portal: #
- Use filters to narrow resources by date range, data type, pathogen or host species, or other conditions
- Search within filters to find specific terms
- Apply multiple filters at once to find results with overlapping properties
- Click “Clear All” to reset results to your original query
- To build more specific queries or narrow your results down even more, use Advanced Search. To learn about Advanced Search, click here.
Last updated on